VISION Developer's Organization
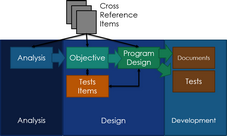
This illustration represents the various sections in VISION Developer:
VISION is organized to support the first three phases of the Instructional Systems Development (ISD) process: Analysis, Design and Development. The colored areas on the illustration represent the three phases.
Notice that the illustration also shows several sections within (and outside) the three areas: Analysis; Objective; Test Items, Program Design; Development - Documents; Development - Tests, and Cross Reference Items.
Information is entered at the analysis module, and flows through the system from left to right, reflecting the classic, systematic approach to the training process.
 See also the following Advisor topic:
See also the following Advisor topic:
The Systematic Approach to Training - Overview
VISION Developer's Function
VISION Developer supports a performance-based approach to the design of training systems. VISION includes a section to help you identify and document the tasks your target audience must do. Related functions assist in establishing the objectives, objective content, test items and curriculum to support the instruction of those tasks.
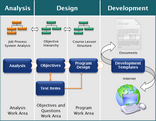
The Development Platform is organized as follows:
Instructional Design Activities
The Three Sections: Analysis, Objective, and Program
Instructional Design Activities
Instructional Design Steps
Remember the five steps in the instructional design process?
1.Analysis
2.Design
3.Development
4.Implementation
5.Evaluation
The VISION development platform directly supports the first three (Analysis, Design, and Development).
The Sections
The illustration above shows how a VISION project database is organized. Notice that it is divided into three sections:
Analysis
This section contains a hierarchical structure that illustrates how a job position is organized with respect to tasks, skills, and knowledge components. The hierarchy identifies a job position, its subordinate areas of responsibility, duties, phases, and the tasks. For each task, the hierarchy expands further to display steps (elements) and skill/knowledge components.
This section will help you to:
•Create Job Analysis Hierarchies.
•Conduct Task Hazard Analysis.
•Select tasks for training.
•Do a Task Analysis.
Objectives and Content
This section contains a hierarchy of terminal and enabling objectives. The objectives are usually developed from the analysis information. Sometimes the objectives are created independent of a task analysis. Each objective contains content objects and test questions. Test questions are linked to their parent objective, but content actually resides within the objective. Together, the objective statement along with its questions, content, and other properties, make that objective a complete learning object. For this reason, the objectives hierarchy is considered a learning object hierarchy.
In this section, you can:
•Create Objective Hierarchies from the task analysis.
•Insert objectives not necessarily based on the task analysis.
•Write formal statements for the objectives and assign various properties to them.
Test Items (Questions)
In this section, VISION stores the test questions that are associated with the objectives. It works like this:
•From an Objective Hierarchy workscreen, you can access another set of workscreens that are specially designed to help you write test questions. You can choose from seven different types of test questions. When you enter a question, VISION will store it in a "question bank," but it will be "linked" to the objective. You can enter questions for every objective in the same manner.
•Later, test questions can be drawn from the question bank by the Test Generator and applied to a test according to parameters that you will define. In this way, you will be using the test question bank to compile tests and answer keys in seconds, rather than hours.
Program Design
This section provides the structure for how the objectives (learning objects) are packaged as a structured training program. You might equate the program to a curriculum. It lists the courses, topics within courses, and the lessons that form a complete program. The program, or curriculum, is an outcome of your design activities in VISION.
This section will help you to:
•Organize a training program structure such as courses, topics and lessons.
•Sequence (assign) objectives into the structure.
Tests
This section represents the VISION Developer "Test Generator." It will help you to produce cognitive tests very quickly by pulling test items from the database and compiling a finished test and answer key. You enter the parameters that define the kind of test you want, and then VISION will generate the test and give you opportunities to refine the selected items.
Cross Reference Items
This feature enables you to set up libraries of cross reference items (for example, a cross reference library might be a list of critical equipment used by the learner). Throughout the project, you can link the items to components in any of the three database sections (for example, you could link critical equipment to tasks). VISION will utilize these links to produce special documents and to support queries and change management activities at a later time.