To decide if an objective should be classified as a recall fact (or recall/procedure, recall/rule, recall/concept, recall/process, recall/principle, consider several key factors. Does the objective meet the definition of a recall objective? How does it compare with examples of other recall objectives? What instructional strategy would be used to teach the objective, and does that strategy make sense? The answers to these questions, and more are provided by the topics below.
Definition of a Fact Objective
A fact can be defined as:
 An arbitrary relationship among objects, symbols or events
An arbitrary relationship among objects, symbols or events
•That cannot be generalized or used to explain anything
 And can be mastered only by directly recalling the information
And can be mastered only by directly recalling the information
Examples of a Fact Objective
•State the mission of the audit department.
•Name the three most heavily populated islands in Indonesia.
•Indicate the location of all 10 fire extinguishers on the floor plan provided.
•List the five emergency steps for a stalled engine.
•Arrange the steps for starting up the main compressor in the correct order.
Typical Action Verbs of Fact Objectives
Below is a list of action verbs for commonly used with recall objectives.
Arrange |
Identify |
Locate |
Place |
Sort |
Choose |
Indicate |
Name |
Quote |
State |
Cite |
Label |
Note |
Recall |
Underline |
Designate |
List |
Order |
Recite |
|
Instructional Strategy for Fact Objectives
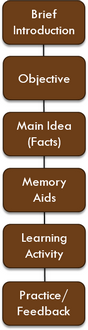
Introduction to an objective: A Brief statement that orients the student to what is coming It also serves as the "glue" that helps the lesson to flow from objective to objective. |
|
Objective: A precise definition of what the student will be capable of doing after the instruction has been completed. For fact objectives, the student will list, state, recite, name, define, draw, label, etc. |
|
Main idea for a fact objective: States exactly what it is to be remembered, including the number of items and the sequence, if applicable. The practice and tests will be based on the learner's ability to recall the information in the main idea. |
|
Memory aids for a fact: Presents the information in simpler terms, relates it to something the learner already knows, or explains how it will be useful in real life. Memory aids are also used to organize or chunk the information into blocks that easier to remember, or graphically illustrate the material in a way that makes it easier to remember. |
|
Special learning activity for a fact: Provides graduated activities that help the learner remember the information in increasingly larger chunks, or with increasingly fewer cues. Sometimes special learning activities provide an opportunity for a more interesting method of remembering the information, such as in a game, puzzle or other application. Feedback provides the correct information at each graduated step. |
|
Practice and feedback for a fact: Requires the learner to perform the recall task exactly as stated in the objective. Feedback provides the complete and correct answer. |