How to Write a Brief Introduction for an Objective
A brief introduction to an objective should have these characteristics:
•Relates the current objective content to what has just been learned.
•Orients the students to what is coming in the segment.
•Motivates the learner by establishing relevance and purpose for learning the material.
Here's an example of a brief introduction to an objective:
In the last segment you became familiar with all of the features and components of the DOP Pentrometer. Now it's time to start using the meter. This segment will cover the first important activity: Calibrating the meter. It is vital to properly calibrate the meter to be sure your are getting accurate readings.
 Note that the introduction is very brief and to the point, while still exhibiting the three components of an introduction: orientation to what was taught before; brief overview of what is coming, and a motivating statement, in this case based on why it is important to learn the material. Note that the introduction is very brief and to the point, while still exhibiting the three components of an introduction: orientation to what was taught before; brief overview of what is coming, and a motivating statement, in this case based on why it is important to learn the material.
|
How to Write a Main Idea for a Structure Objective
To develop instruction for a structure objective:
First, write a lead-in statement that introduces the structure. The lead-in statement should basically be a restatement of the objective behavior.
|
One aspect of a structure objective is to identify the parts, elements or components of the object.
For example, the major parts of a bicycle are the frame, gears, derailleurs, brakes, headset, handlebars, seat, front fork, wheels, wheel hubs, chain, bottom bracket and petals.
|
Describe the function of each identified component. The function refers to what each part does to contribute to the whole. For example, the function of the chain is to transfer energy to the wheels through gears.
|
How the parts of a structure fit together is an important aspect of the structure itself. This is almost always shown with a picture or illustration. For example, below is shown how a bike chain fits into the gears and derailleur.
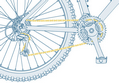
|
How to Write an Explanation for a Structure Objective
Here are some suggestions for the explanation component of your use structure objective:
Clarify the function or characteristics of any critical component in the structure. Explain the role or characteristics of a component if it is fundamental to understanding the structure.
For example, in a bicycle braking system, it is important that the learner understand that by squeezing the handlebar brake lever, a cable connected to the brake set is retracted, which operates the braking mechanism, which pinches the wheel between the brake pads, causing friction which slows the revolution of the wheel.
|
Point out any common malfunction or unusual configurations in the structure; what causes them, how they affect the overall structure.
Some structures are interrupted or foiled by common malfunctions. For the bicycle brake example, you might point out problems like this; "If the brake pads are not periodically inspected and replaced, the pads will wear down, and be less effective in slowing the wheel."
|
Use models, graphics, photographs, actual equipment, or other aids to highlight the details of the structure. These help the learner understand how the structure is really put together.
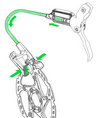
|
How to Develop a Practice for a Structure Objective
Here are some ways you can provide challenging practice for a use structure objective:
•Provide learners with details about specific parts in the structure and ask them to identify the part, its purpose, and any common malfunctions or issues.
•Provide examples of malfunctions or variant events and ask them to identify the possible cause.
Either way, your practice section should:
•Increase the difficulty of the practice questions to challenge the learner's understanding.
Provide general instructions to the student (or to the instructor, if the practice will be administered by an instructor) for how to carry out the practice. Instructions should include things like: where to get equipment, how to use the lesson guide, and who to see for help.
Start the practice instructions with a clear statement of what the learner will do in the practice.
|
Be sure to describe the expected outcomes so that the student can tell if they are on the right track at every step.
|
Provide several different practice exercises to cover the range of instances required to ensure the student understands the objective and can apply it in the range of circumstances likely to be encountered.
|
Provide feedback after every instance or repetition. Practice without feedback is practically useless!
Include feedback after each question that explains "why". Explain why the objective, or any part of the objective, works the way it does.
|

 Note that the introduction is very brief and to the point, while still exhibiting the three components of an introduction: orientation to what was taught before; brief overview of what is coming, and a motivating statement, in this case based on why it is important to learn the material.
Note that the introduction is very brief and to the point, while still exhibiting the three components of an introduction: orientation to what was taught before; brief overview of what is coming, and a motivating statement, in this case based on why it is important to learn the material.
