The best way to consolidate the D-I-F data is to compute an average. As a result, you should have three values for each task:
D: Represents the difficulty of the task.
I: Represents its importance in considering the consequences of an error or omission.
F: Represents the frequency that the task is performed.
The D-I-F data is usually collected in numeric form on a scale from 1 to 5 (VISION allows a range of 0 – 6 as well as a range from 0-9.99, to accommodate other scales) for each variable. Sometimes the information is collected by distributing a questionnaire, such as VISION’s "Task DIF Survey" report (on the Main Menu,select Outcomes and then VISION Report. Then click on the Analysis tab and select "Task DIF Survey"); other times it is gathered through a guided consensus meeting.
The D-I-F Algorithm
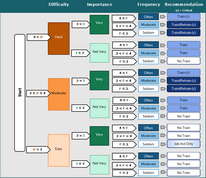
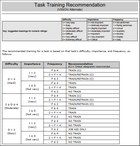
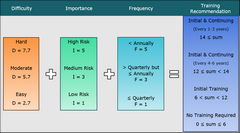
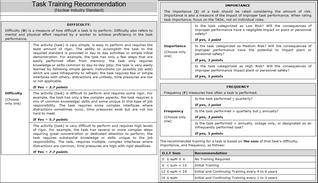
The “Task Training Recommendation” report applies a built-in algorithm to recommend a degree of training for each task according to your assessments of the task’s difficulty, importance, and frequency of performance (D-I-F):
•Train
•Recurring Training (Train / Retrain)
•No Training Required
Review each recommendation carefully, get consensus from the appropriate personnel, and change any notation according to your team’s evaluation.
VISION Standard
Each task's Difficulty, Importance, and Frequency is estimated on a 1 to 5 scale, where 1 is the least difficult, least important, and most frequently performed; and 5 is the most difficult, most important, and least frequently performed.
VISION Alternate
This algorithm is similar to the VISION Standard, but the scale is wider, 0 to 6. 0 Is the least difficult, least important and most frequently performed; and 6 is the most difficult, most important, and most frequently performed.
The VISION Alternate algorithm is the same as VISION Standard algorithm.
Nuclear Industry Standard
Each section in this algorithm is assigned a specific point value, where the lowest values are assigned to the least difficult, least important and most frequently done sections, and the highest are assigned to the most difficult, most important, and least frequently performed. Once point values are assigned, they are added together, and that sum determines the training recommendation.
What are the Implications of NOT Selecting a Task for Training?
If you select "No", the task is not selected for training and the following implications apply:
•You can still analyze the task to identify Elements (steps) and key Skills/Knowledge components.
•You can use task analysis information to produce procedures and a Task Qualification Checklist document for the task.
•You can create objectives for Elements and Skills/Knowledge components under a task, but the objectives will not be listed on an Analysis report.
•Although you cannot write an objective directly for a task that has not been selected for training, this does not mean that you should select the task for training just so you can create an objective or consolidate the task. Careful consideration must be taken before selecting a task for training.